Summary: What is OCEN all about? This article is a quick guide on how OCEN works. We also look at the key players in the OCEN ecosystem and the numerous benefits it has to offer to the lending ecosystem, particularly to the MSME sector.
- What is OCEN?
- What is the idea behind OCEN?
- How does OCEN work?
- The benefits of OCEN
- How OCEN is impacting India’s MSME lending ecosystem
- OCEN will be instrumental in the rise of the credit marketplace
The financial services sector in India has undergone a massive transformation in recent years. Along with the application of pioneering technologies, the introduction and adoption of India Stack — a framework of open APIs and digital public goods has significantly contributed to improving financial inclusion in the country.
With a primary objective to standardise and democratise access to credit, the Open Credit Enablement Network (OCEN) was launched in 2020 to create a ‘UPI for credit’ for Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs). Driving the larger vision of India Stack, OCEN was launched to revolutionise how credit is distributed to end-users. In this blog post, we will understand all about OCEN and how it is a major step in the right direction for the democratisation of credit in India.
What is OCEN?
OCEN is a decentralised open credit network that introduces new touchpoints for financial services distribution.
As a part of the larger framework of India Stack’s open APIs, OCEN is reimagining the lending value chain, allowing lenders and borrowers to come on the same platform and interact easily.
“India needs to go that extra mile in offering credit to the most deserving, smallest businesses and individuals. With most credit directed to large companies in large volumes, smaller companies and micro enterprises are left in the lurch with little or no access to credit at all which is a huge concern for the next growth phase of the industry.”
Nandan Nilekani: Co-Founder and Non-Executive Chairman of the Board of Infosys
What is the idea behind OCEN?
Over the last decade, the last-mile finance marketplace has experienced a paradigm shift. Having said that, there was a growing need for a standardised framework in the lending value chain.
Developed with the aim to facilitate the various aspects of the lending value chain — India’s Open Credit Enablement Network, establishes a universal protocol to further safeguard and strengthen last-mile borrowers’ credit access.
OCEN is empowering technology ecosystem participants to embed loan products on their platforms while borrowers can now easily interact with lenders such as loan service providers and account aggregators.
How does OCEN work?
As a credit protocol infrastructure, OCEN acts as a middle layer between lenders and online lending services.
With OCEN, the flow of credit between various participants in the ecosystem like borrowers, lenders, and credit distributors is codified under a common set of standards.
These standards allow participants of the credit ecosystem to connect with one another without having to build bespoke APIs and infrastructure.
Prior to the introduction of OCEN, digital platforms had a very high barrier to entry for offering financial services. OCEN’s standardised API architecture has an API for each step of the lending lifecycle. Digital platforms can now integrate these APIs, collaborate with multiple lenders, and digitise the end-to-end lending lifecycle. By leveraging OCEN’s framework of APIs, lenders now have the option to approach multiple digital platforms and expand their pool of borrowers.
The key stakeholders in the OCEN ecosystem are:
- Loan Service Providers (LSPs): A loan service provider is any digital platform that has a pool of borrowers looking to avail credit facilities.
- Technology Service Providers (TSPs): TSPs are FinTech companies that facilitate the onboarding of lenders and digital platforms onto the OCEN protocol for the successful rollout of credit programs to borrowers.
- Lenders: These include financial institutions like banks and Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs) with access to core banking networks and looking to offer credit lines to borrowers.
- Borrowers: Borrowers could be either MSMEs or Individuals who leverage credit lines available on digital platforms.
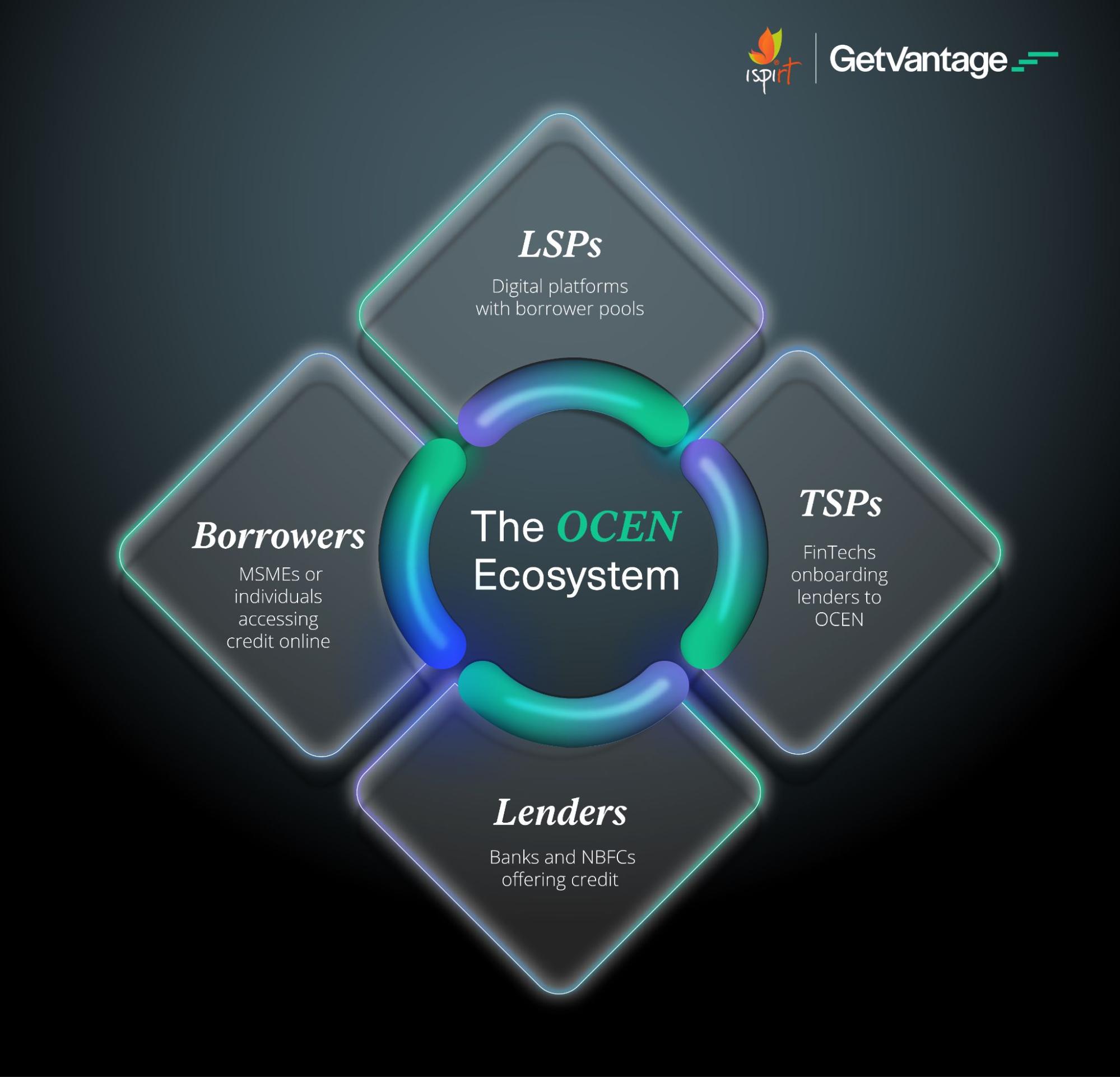
While the lenders deploy the capital, the TSPs provide advanced plug-and-play capabilities to reduce entry barriers for offering credit. With OCEN, LSPs can augment their offerings by enabling a range of credit services for borrowers on digital platforms.
The benefits of OCEN

OCEN has enabled the entire lending flow to be implemented digitally, connecting marketplaces and aiding with the creation of innovative financial products for last-mile borrowers.
Some of the many benefits of OCEN include:
- OCEN has helped standardise the lending infrastructure, streamlining everything right from applying for a loan to its processing, eliminating bureaucratic hurdles and saving time.
- By offering a digital acquisition channel, OCEN automates the interaction between lenders and borrowers.
- Backed by a robust credit infrastructure, lenders can reduce their risk exposure, leading to competitive interest rates and in turn making credit more affordable for borrowers.
- OCEN facilitates quick access to credit and lowers turnaround times.
- Its real-time data access reduces the risk of default by empowering lenders to make informed decisions based on comprehensive borrower information.
How OCEN is impacting India’s MSME lending ecosystem

The 64 million MSMEs in India are up against a credit gap of INR 20 – 25 trillion. Less than 11% of MSMEs have access to formal credit.
The historically unorganised nature of India’s MSME sector, together with a dearth of requisite data trails for establishing creditworthiness, has only added to the problem.
OCEN has been built to innovate the entire loan process. It is expected to bring about monumental changes to the lending side of the financial services industry. While the platform creates healthy competition among lenders, it opens up greater access to credit at the most competitive rates with shorter turnaround times.
MSMEs can build credit profiles and unlock credit more aligned with their financial cycles. On the other hand, financial institutions can access a larger pool of MSME borrowers who can easily apply for interday and intraday loans through LSPs, simply by sharing their business transaction history.
OCEN will be instrumental in the rise of the credit marketplace
The innovative concept of OCEN paves the way for countless lending opportunities.
LSPs are now uniquely positioned to distribute timely credit to their customers and make much-needed additions to the lending value chain to make it more inclusive.
With OCEN, providing the necessary infrastructure, insights, and advanced analytics to develop innovative lending products, we expect it to further encourage new players to step up and play crucial roles in the delivery of credit.


